DevOps Guide: Meaning, Tools, Lifecycle & Careers

Senior WebCoder
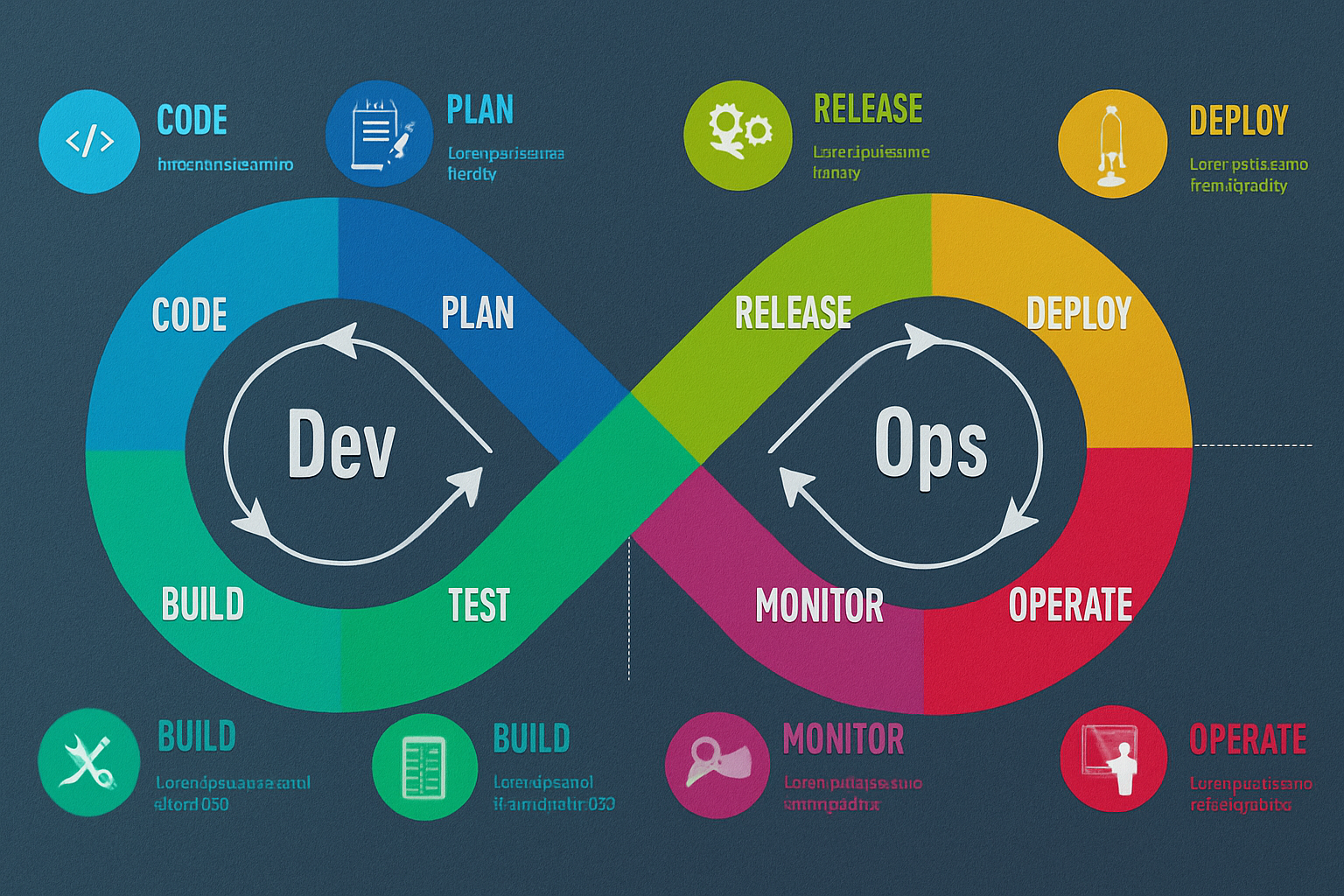
DevOps has become essential for businesses looking to deliver software quickly, efficiently, and reliably. This guide will walk you through what DevOps is, why it matters, how it works, and how to start or advance your DevOps career.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to shorten the software development lifecycle while delivering high-quality applications continuously.
DevOps is not a tool, but a culture focused on collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement.
Why DevOps Matters
- Faster Delivery: Releases go from months to days or even hours.
- Improved Collaboration: Breaks silos between developers, testers, and ops.
- Higher Quality: Automation reduces human error and increases consistency.
- Customer Satisfaction: Frequent and reliable updates improve user experience.
- Cost Efficiency: Automated infrastructure reduces overhead costs.
DevOps Lifecycle (Phases)
- Plan – Define project goals, requirements, and timelines.
- Develop – Write code using version control systems like Git.
- Build – Compile code and manage dependencies.
- Test – Perform automated unit and integration testing.
- Release – Deploy to production using CI/CD pipelines.
- Deploy – Roll out using blue-green or canary deployments.
- Operate – Monitor infrastructure and application health.
- Monitor – Track logs, performance, and user feedback.
These phases are continuous and cyclical, not linear.
Popular DevOps Tools (by Category)
| Category | Tools |
|---|---|
| Version Control | Git, GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket |
| CI/CD | Jenkins, GitHub Actions, CircleCI, GitLab CI, Travis CI |
| Configuration | Ansible, Chef, Puppet |
| Containerization | Docker, Podman |
| Orchestration | Kubernetes, OpenShift |
| Monitoring | Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, Datadog |
| Cloud Platforms | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud (GCP) |
| Infrastructure | Terraform, Pulumi |
DevOps vs Traditional IT
| Feature | Traditional IT | DevOps |
|---|---|---|
| Development & Ops Teams | Separate | Unified |
| Release Frequency | Monthly or Quarterly | Daily or On-Demand |
| Manual Processes | High | Low (automation preferred) |
| Collaboration | Low | High |
| Feedback Cycle | Slow | Fast |
DevOps Best Practices
- Use CI/CD pipelines to automate builds, tests, and deployments.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) using tools like Terraform or Ansible.
- Automated testing for unit, integration, and security.
- Monitoring and Logging to gain visibility into systems.
- Security Integration (DevSecOps) from the start of development.
- Frequent small releases instead of big-bang deployments.
- Cultural collaboration between Dev, QA, and Ops teams.
How to Start:
- Learn the basics of Linux, Git, and scripting.
- Pick a programming language (e.g., Python).
- Practice with Docker and Kubernetes.
- Build CI/CD pipelines using GitHub Actions or Jenkins.
- Automate infrastructure using Terraform.
- Deploy projects to AWS or Azure.
- Stay updated with DevOps blogs and communities.
DevOps in the Cloud
Cloud computing has accelerated DevOps adoption. Services like AWS CodePipeline, Azure DevOps, and Google Cloud Build help automate and scale deployments.
Benefits:
- Scalability
- Cost savings
- Global accessibility
- Integrated security tools
Real-World Use Cases
- Netflix: Uses DevOps for continuous delivery and auto-scaling infrastructure.
- Amazon: Thousands of deployments daily with zero downtime.
- Spotify: Agile teams deploy frequently using microservices architecture.
Common DevOps Challenges
- Resistance to cultural change
- Tool overload (too many options)
- Legacy systems integration
- Lack of automation experience
- Inconsistent environments (Dev ≠ Prod)
Conclusion
DevOps is more than tools—it's a mindset that fosters collaboration, automation, and rapid delivery. It enables teams to deliver better software, faster and more reliably.
Whether you're a developer, sysadmin, or aspiring engineer, DevOps skills are in high demand and will continue to shape the future of IT.

Gokila Manickam
Senior WebCoder
Gokila Manickam is a Senior WebCoder at FUEiNT, contributing expert insights on technology, development, and digital strategy.
