Pagination vs Load More vs Infinite Scroll: Which is Best?

Senior WebCoder
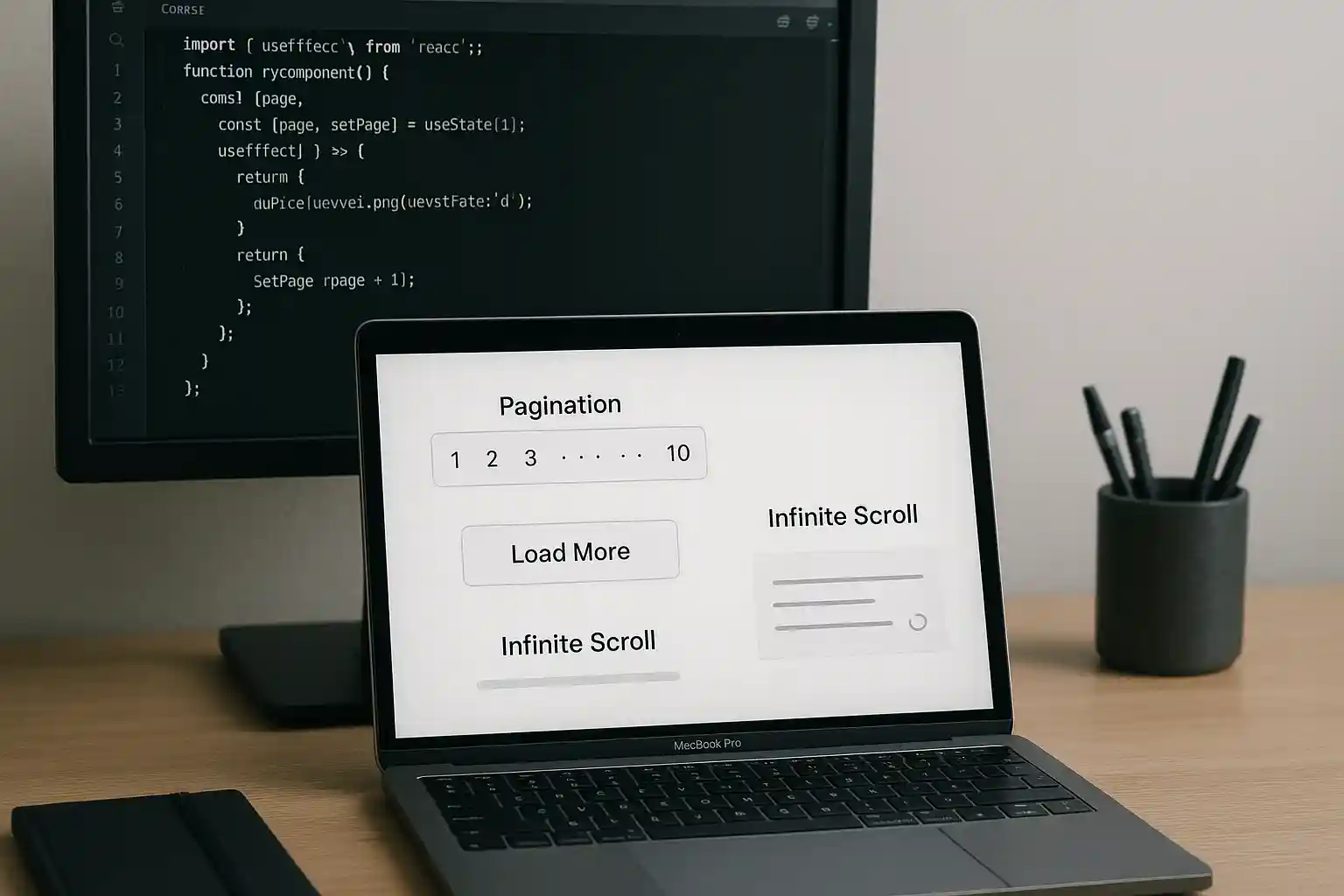
Which is Best in 2025?
Pagination vs Load More vs Infinite Scroll: When building websites with large content libraries, you'll face a critical decision: which pagination strategy works best for SEO? The choice between pagination, load more buttons, and infinite scroll significantly impacts your search rankings. Furthermore, this decision affects user experience, mobile performance, and analytics tracking. In this guide, we explore each pagination method's SEO advantages and disadvantages. Moreover, we provide actionable implementation steps. Most importantly, we help you select the right pagination strategy for your specific needs.
Understanding Pagination: Traditional URL-Based Content Loading
Pagination divides content into separate pages, each with its own unique URL. This traditional approach has remained popular for organizing archives, e-commerce listings, and search results for good reason. First, pagination is straightforward to implement and provides clear navigation for both users and search engines. Additionally, each page functions as an independent entity in the search index. This makes it easier to track performance and user behavior across different content segments.
Pagination Pros:
- Each page receives a unique, crawlable URL that search engines index individually
- Supports canonical tags and rel="next"/"prev" markup for proper link consolidation
- Users can bookmark, share, or deep-link to specific pages within archives
- Clear analytics tracking shows user flow and conversion patterns
- Works reliably with SEO tools and frameworks with minimal configuration
Pagination Cons:
- Multiple page loads increase clicks required for users browsing content
- Poor navigation design fragments ranking signals if internal linking isn't managed correctly
- Feels less modern compared to seamless loading experiences
- Requires careful canonical tag strategy to prevent duplicate content issues
Load More Buttons: Balancing Modern UX with SEO
Load more buttons allow users to retrieve additional content on-demand by clicking. This method bridges traditional pagination and modern seamless experiences. Importantly, content loads dynamically without page reloads. As a result, users maintain control over content consumption, which improves engagement and reduces mobile data usage. When implemented with proper URL updates, load more buttons achieve strong SEO performance while delivering responsive interfaces.
Load More Button Pros:
- Mobile-friendly interaction requiring just one tap instead of multiple navigation clicks
- Reduces initial page load time by fetching content in chunks
- Supports SEO through dynamic URL updates with proper History API implementation
- Provides users control over content loading, improving perceived performance
- Works effectively for both desktop and mobile-first designs
Load More Button Cons:
- Content loaded after the initial click may remain invisible to search engines without URL updates
- Deep linking and bookmarking to partially loaded content proves difficult without special implementation
- Requires careful JavaScript handling and progressive enhancement for accessibility
- Analytics tracking becomes complex, distinguishing initial pageviews from dynamic content loads
- Demands disciplined development to maintain crawlable content and prevent indexing gaps
Infinite Scroll: Engagement vs. SEO Trade-offs
Infinite scroll automatically loads new content as users reach the bottom of the current view. This creates a continuous, uninterrupted feed. Consequently, this approach dominates social platforms, image galleries, and content-heavy applications. Additionally, infinite scroll prioritizes user engagement and time-on-page metrics. However, it introduces significant technical challenges for SEO and accessibility if not carefully designed.
Infinite Scroll Pros:
- Delivers seamless user experience encouraging extended browsing and engagement
- Particularly effective for social media feeds, portfolios, and image galleries
- Eliminates friction by removing clicks between content chunks
- Boosts engagement metrics and time-on-page when implemented thoughtfully
- Creates naturally flowing experiences that users find intuitive
Infinite Scroll Cons:
- Content beyond the initial view remains invisible to search engines by default
- Bookmarking and deep linking to specific content becomes nearly impossible
- Analytics become unreliable for user sessions, conversions, and funnel tracking
- Accessibility suffers significantly—keyboard navigation traps users, footers become unreachable
- Requires advanced technical solutions like hybrid pagination or server-side rendering for effective SEO
SEO Performance Comparison Table
| Pagination Strategy | SEO Rating | Mobile Experience | Setup Difficulty | Analytics Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pagination | Excellent | Good | Low | Excellent |
| Load More | Good (with URL updates) | Excellent | Medium | Good |
| Infinite Scroll | Poor (by default) | Excellent | High | Poor |
Implementing Each Pagination Strategy for Maximum SEO Impact
Pagination Implementation Steps:
- Use rel="next" and rel="prev" link elements to inform search engines about series relationships
- Implement canonical tags pointing to paginated versions, not "view all" pages
- Ensure internal linking encourages crawlers to discover and index all pages
Load More Button Implementation Steps:
- Update browser URLs with History API (pushState/replaceState) when content loads
- Maintain consistent query parameters (like
?page=2or?offset=20) for discoverability - Test with Google Search Console's URL Inspection tool to verify crawling
Infinite Scroll Implementation Steps:
- Combine infinite scroll with paginated fallback URLs for browser and crawler compatibility
- Use server-side rendering to populate initial pages with meaningful content
- Implement rel="next" on initial pages to guide crawlers through remaining content
Selecting Your Best Pagination Strategy
Choose Pagination when: Operating e-commerce sites, research databases, or content archives where SEO visibility and deep linking matter. Every page must be findable and rankable individually.
Choose Load More when: Prioritizing modern UX and mobile responsiveness while maintaining SEO strength. Your team can commit to proper URL management and testing throughout development.
Choose Infinite Scroll when: Engagement and user retention are primary metrics, with SEO as secondary priority. You have technical resources to implement hybrid approaches or server-side rendering.
Testing Your Pagination Implementation
- Crawl your site as Googlebot using Screaming Frog to verify all content accessibility
- Test with Google Search Console's URL Inspection to confirm indexing of paginated content
- Monitor Core Web Vitals to ensure pagination strategy doesn't negatively impact page speed
- Validate canonical tags, rel="next"/"prev", and internal linking with SEO auditing tools
- Audit analytics implementation to ensure accurate tracking across pagination methods
Common Pagination Questions Answered
1. Does Infinite Scroll Work with Google SEO Rankings?
Yes, but only when paired with hybrid pagination, server-side rendering, or crawlable URLs. Most implementations lack these safeguards, making pagination or load more buttons significantly safer SEO choices.
2. Which Pagination Method Works Best on Mobile?
Load more and infinite scroll feel more native on mobile devices. However, load more with proper URL updates offers the ideal balance between mobile user experience and SEO performance.
3. Is rel="next" and rel="prev" Required for Pagination?
Yes, it's essential best practice. These tags help Google understand page relationships and consolidate ranking signals across paginated series.
4. How Does Load More Affect SEO Without URL Updates?
Negatively. Content loaded dynamically remains invisible to search engines unless you update the browser URL with each load using the History API.
5. How Should Analytics Track Infinite Scroll or Load More?
Switch to event-based analytics using Google Analytics 4. Track "content_load" or "load_more_click" events separately from traditional pageviews to capture accurate user behavior.
Making Your Final Pagination Decision
Most businesses balancing SEO with user experience should choose pagination as their primary strategy. Load more buttons offer compelling middle ground when mobile user experience remains important. Infinite scroll works best for engagement-focused platforms where organic search traffic plays a secondary role. Evaluate your specific content structure, team capabilities, and business goals carefully.
This comprehensive guide reflects 2025 SEO best practices. It provides actionable recommendations for developers, site owners, and digital marketers. Choose your pagination strategy wisely to maximize both search visibility and user satisfaction.
Related SEO and Content Loading Topics
Learn more about optimizing your website's content discovery:
- Pagination best practices for e-commerce SEO
- Load more buttons vs traditional pagination
- Infinite scroll SEO implementation guide
- URL structure for paginated content
- Canonical tags and duplicate content
- Internal linking strategy for pagination
- Mobile-first pagination design
- Server-side rendering for dynamic content
- Google Search Console pagination testing
- AJAX crawlability and SEO

Abinesh S
Senior WebCoder
Senior WebCoder at FUEiNT, specializing in advanced frontend architecture, Next.js, and performance optimization. Passionate about determining the best tools for the job.
