Elasticsearch Guide: Purpose, Architecture & Real-World Use Cases

Senior WebCoder

In the era of big data, finding specific information within millions of records in milliseconds is a challenge. This is where Elasticsearch comes into play. As a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine, it has become the gold standard for modern applications.
What is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is an open-source, distributed search and analytics engine built on top of Apache Lucene. It is designed for horizontal scalability, reliability, and real-time search capabilities. It allows you to store, search, and analyze huge volumes of data quickly and in near real-time.
Elasticsearch is the "E" in the famous ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana), often used for centralized logging and monitoring.

Why Use Elasticsearch?
- Real-Time Performance: It provides near-instant search results, making it ideal for search-as-you-type features.
- Scalability: Easily scales from a single node to hundreds as your data grows.
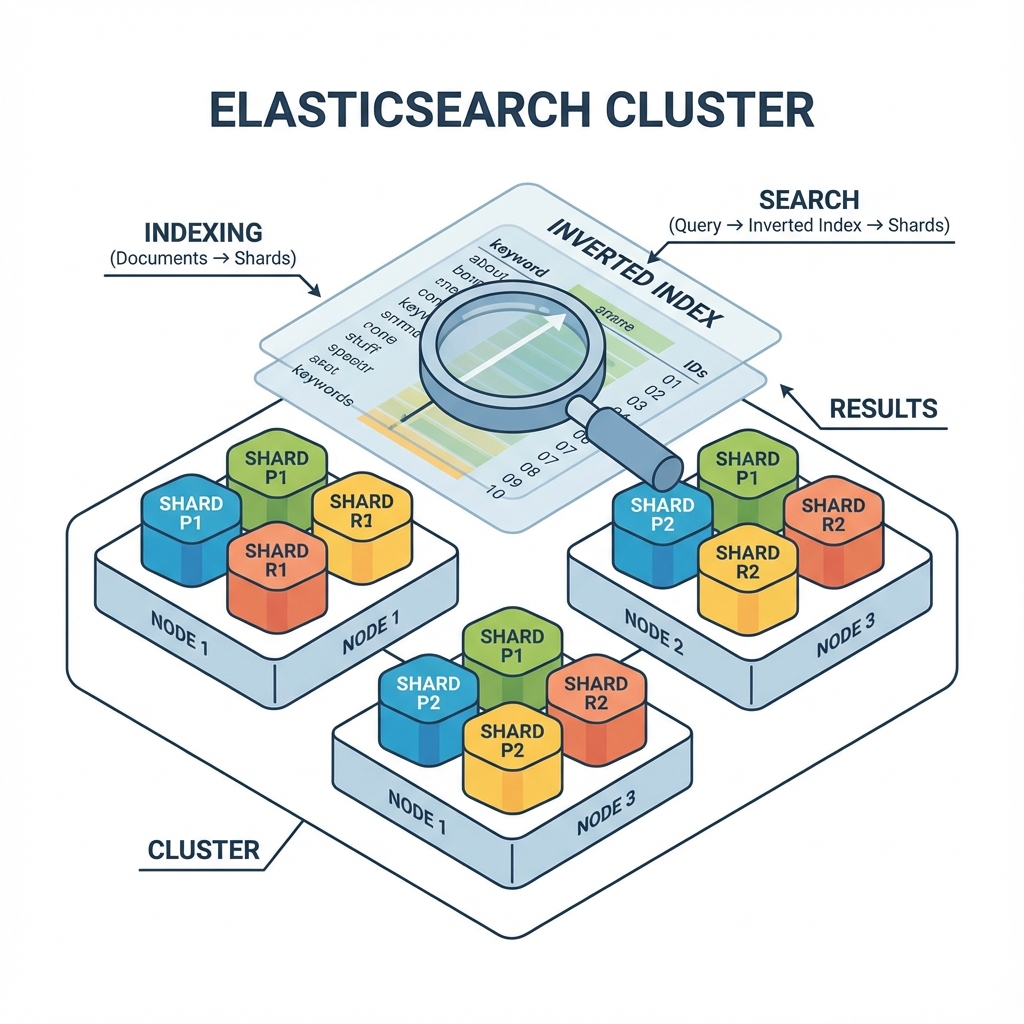
- Distributed Nature: Documents are distributed across different containers (shards), providing redundancy and high availability.
- Schema-Free: It stores data in JSON documents, allowing for flexibility without rigid database schemas.
- Powerful Full-Text Search: It handles complex queries, including "fuzzy" searches, synonyms, and multi-language support.
How Elasticsearch Works (The Basics)
To understand its power, you need to know a few core concepts:
- Inverted Index: Unlike traditional databases that map rows to columns, Elasticsearch uses an "inverted index" that maps words to their locations in documents. This is what makes search so fast.
- Documents & Indices: Data is stored as JSON Documents, which are grouped into Indices (similar to tables in SQL).
- Sharding & Replication: Large indices are split into Shards across multiple nodes. Replicas provide copies for failover and increased search performance.
Technical Comparison: SQL vs Elasticsearch
| Feature | Relational DB (SQL) | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|---|
| Logic | Rows, Columns, Tables | Documents, Types, Indices |
| Search Speed | Slower on large text | Extremely fast full-text search |
| Data Structure | Structured (Schema) | Semi-structured (JSON) |
| Scalability | Vertical (Mostly) | Horizontal (Built-in) |

Real-World Use Cases
Elasticsearch is used across various industries for diverse needs:
1. Application Search
Most modern websites (like E-commerce platforms) use Elasticsearch to power their search bars. It handles auto-complete, filters, and relevance ranking effortlessly.
2. Logging and Log Analytics
DevOps teams use it to aggregate logs from servers, applications, and network devices. Analyzing these logs in real-time helps in identifying bugs or security threats immediately.
3. Business Intelligence & Analytics
Companies use it to build dashboards that monitor sales trends, user behavior, and system performance in real-time.
4. Infrastructure Monitoring
Monitoring the health of complex IT infrastructure by collecting and analyzing metrics like CPU usage, memory, and network traffic.
Companies Using Elasticsearch
- Netflix: Monitors and analyzes customer service operations and security logs.
- Uber: Powers the real-time marketplace, matching riders with drivers.
- GitHub: Uses it to search across billions of lines of code.
- eBay: Searches through millions of product listings with low latency.
Conclusion
Elasticsearch is more than just a search bar; it is a versatile engine for search, logging, and analytics. Its ability to scale horizontally and provide real-time insights makes it an indispensable tool for any data-driven organization.
Whether you are building a simple website or a complex big-data platform, understanding and implementing Elasticsearch can significantly improve your application's speed and user experience.

Gokila Manickam
Senior WebCoder
Gokila Manickam is a Senior WebCoder at FUEiNT, contributing expert insights on technology, development, and digital strategy.
