Edge Rendering vs Traditional Server Rendering

Which One Is Right for Modern Web Applications?
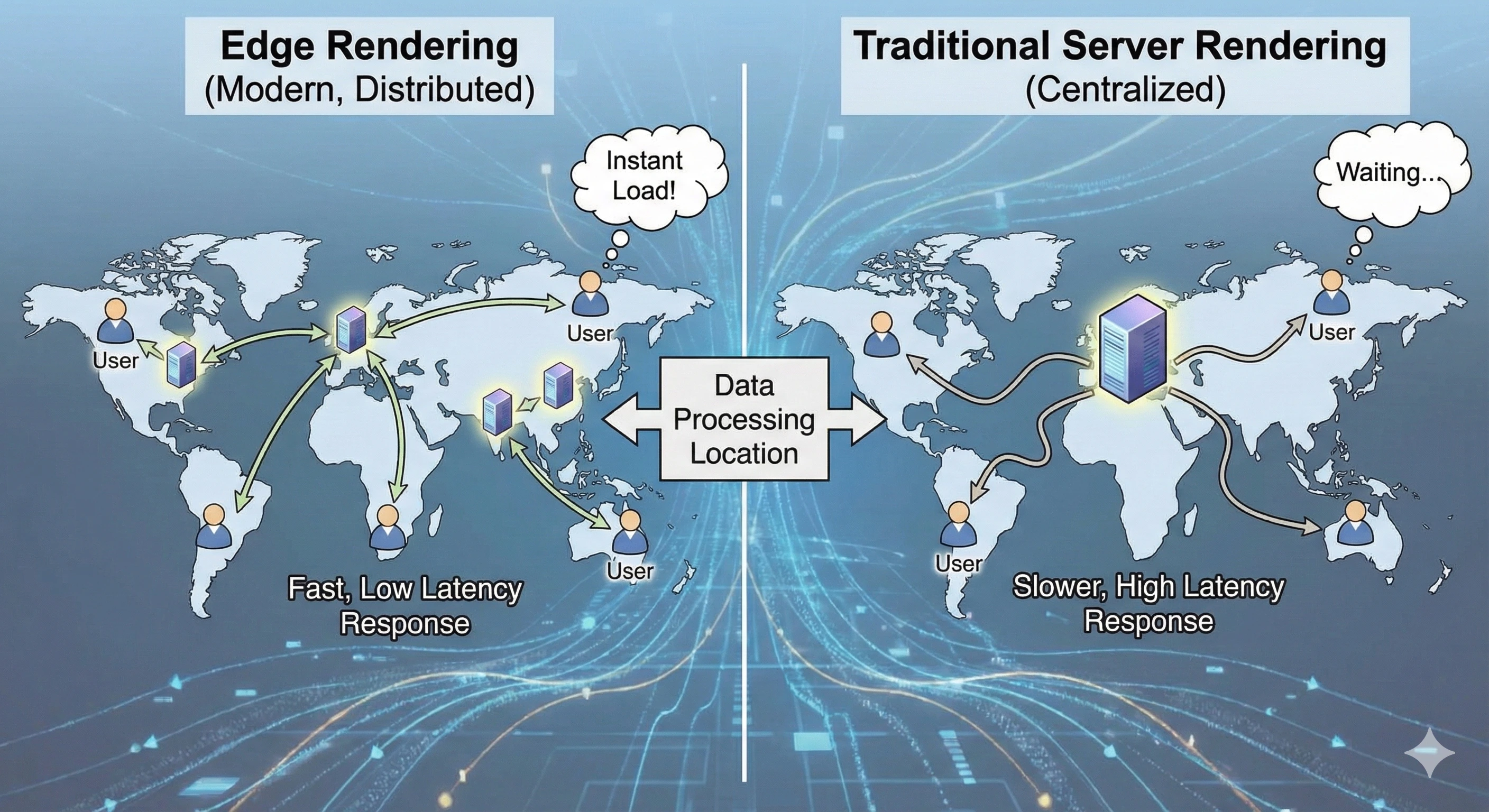
Website speed is no longer optional. Users expect fast page loads regardless of their location. To meet these expectations, modern frameworks like Next.js introduced Edge Rendering, which changes how pages are delivered compared to Traditional Server Rendering.
This document explains both approaches in a simple and readable way, helping you understand when and why to use each one.
What Is Traditional Server Rendering?
Traditional Server Rendering, often called SSR, means that a page is rendered on a central server each time a user requests it.
How Traditional Server Rendering Works
A user requests a page.
- The request is sent to a centralized server.
- The server generates the HTML.
- The HTML is sent back to the browser.
This method has been used for many years in technologies such as PHP, Express.js, and earlier versions of Next.js.
Advantages of Traditional Server Rendering
- It provides good search engine optimization.
- It supports dynamic content easily.
- It is simple to understand and implement.
- It works well for small to medium-sized applications.
Limitations of Traditional Server Rendering
- Performance depends on the distance between the user and the server.
- Server load increases with traffic.
- Scaling can become costly.
- Response time increases for global users.
- When users are far from the server location, page loading becomes slower.
What Is Edge Rendering?
Edge Rendering runs rendering logic on servers located closer to the user, known as edge servers. Instead of relying on one central server, requests are handled by a nearby server.
How Edge Rendering Works
A user requests a page. The request is routed to the nearest edge server. The HTML is generated at that location. The response reaches the user faster.
Edge Rendering is supported by platforms such as Next.js Edge Runtime, Vercel Edge Functions, and Cloudflare Workers.
Why Edge Rendering Is Faster
The main difference between Edge Rendering and Traditional Server Rendering is physical distance.
In traditional rendering, the request travels to a distant server and back. In edge rendering, the request is processed near the user.
Shorter distance reduces latency, which results in faster page loads and better user experience, especially for global audiences.
Comparison Between Edge Rendering and Traditional Server Rendering
- Traditional Server Rendering uses centralized servers, while Edge Rendering uses globally distributed servers.
- Traditional rendering has moderate speed, while Edge Rendering is significantly faster.
- Latency is higher in traditional rendering and much lower in edge rendering.
- Scalability is limited in traditional rendering but highly efficient in edge rendering.
- Traditional rendering may result in higher infrastructure costs compared to edge rendering.
- Both support personalization, but edge rendering performs better at scale.
When to Use Traditional Server Rendering
Traditional Server Rendering is suitable when the application is region-specific, when full Node.js APIs are required, or when the backend logic is complex.
It works well for internal tools, admin dashboards, and small business websites.
When to Use Edge Rendering
Edge Rendering is ideal when the application serves users across different regions and performance is critical.
It is commonly used for marketing websites, SaaS landing pages, e-commerce product pages, authentication checks, and personalization features.
Edge Rendering in Next.js
In Next.js, Edge Rendering can be enabled by specifying the runtime as edge in the page or route configuration. This instructs Next.js to run the code on edge servers instead of traditional servers.
Limitations of Edge Rendering
Edge Rendering has limited access to Node.js APIs. File system access is not available. Some libraries may not be compatible. There are execution and memory limits.
Because of these limitations, Edge Rendering is often combined with traditional rendering.
Conclusion
Traditional Server Rendering laid the foundation for dynamic web applications. Edge Rendering improves performance by bringing computation closer to users.
If your goal is faster load times, improved global performance, and better scalability, Edge Rendering is a strong choice. However, the best solution depends on the application’s requirements, complexity, and audience.
Choosing the right rendering strategy ensures both performance and maintainability.

Praveenkumar M
WebCoder
Praveenkumar M is a WebCoder at FUEiNT, contributing expert insights on technology, development, and digital strategy.
